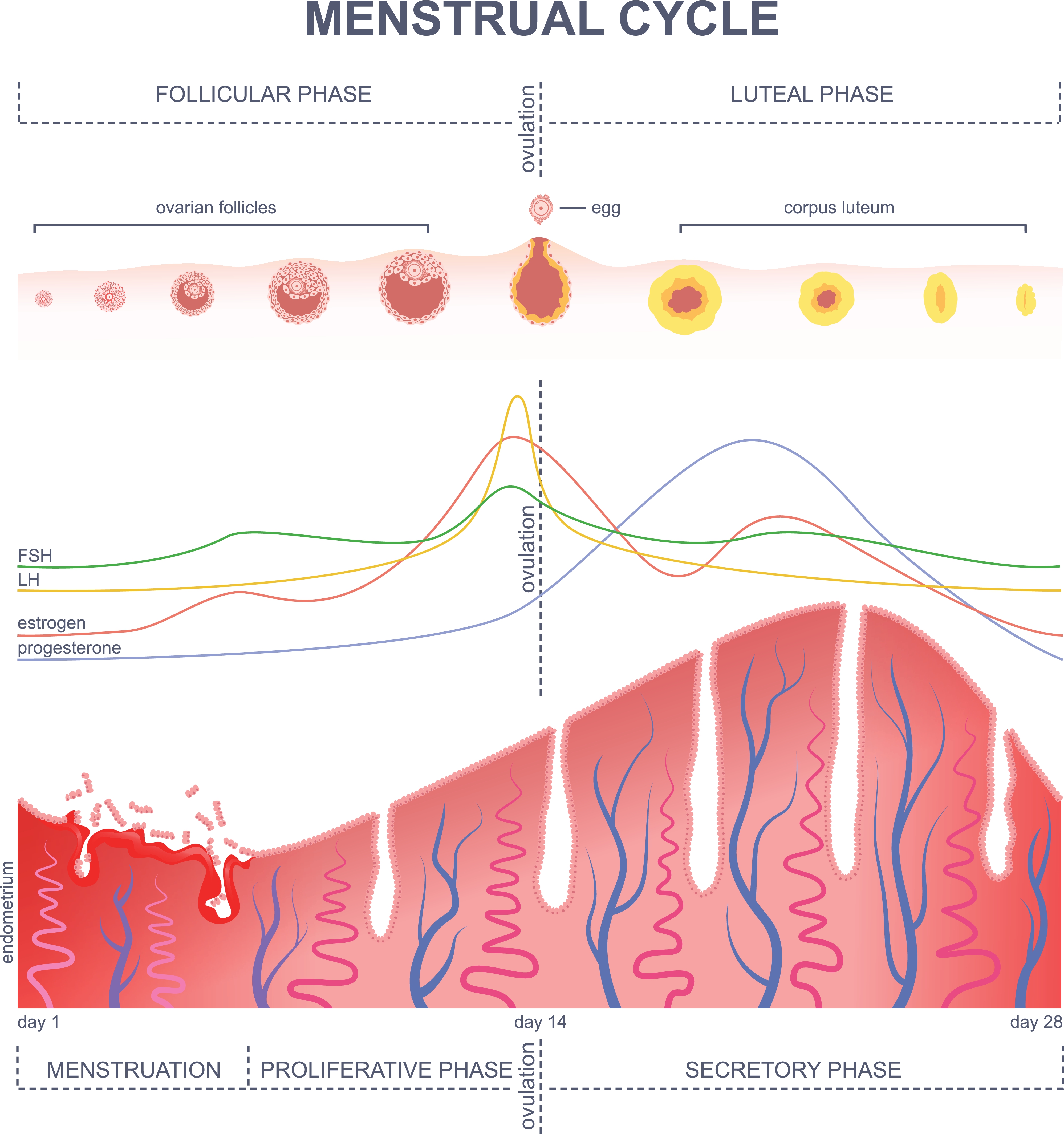
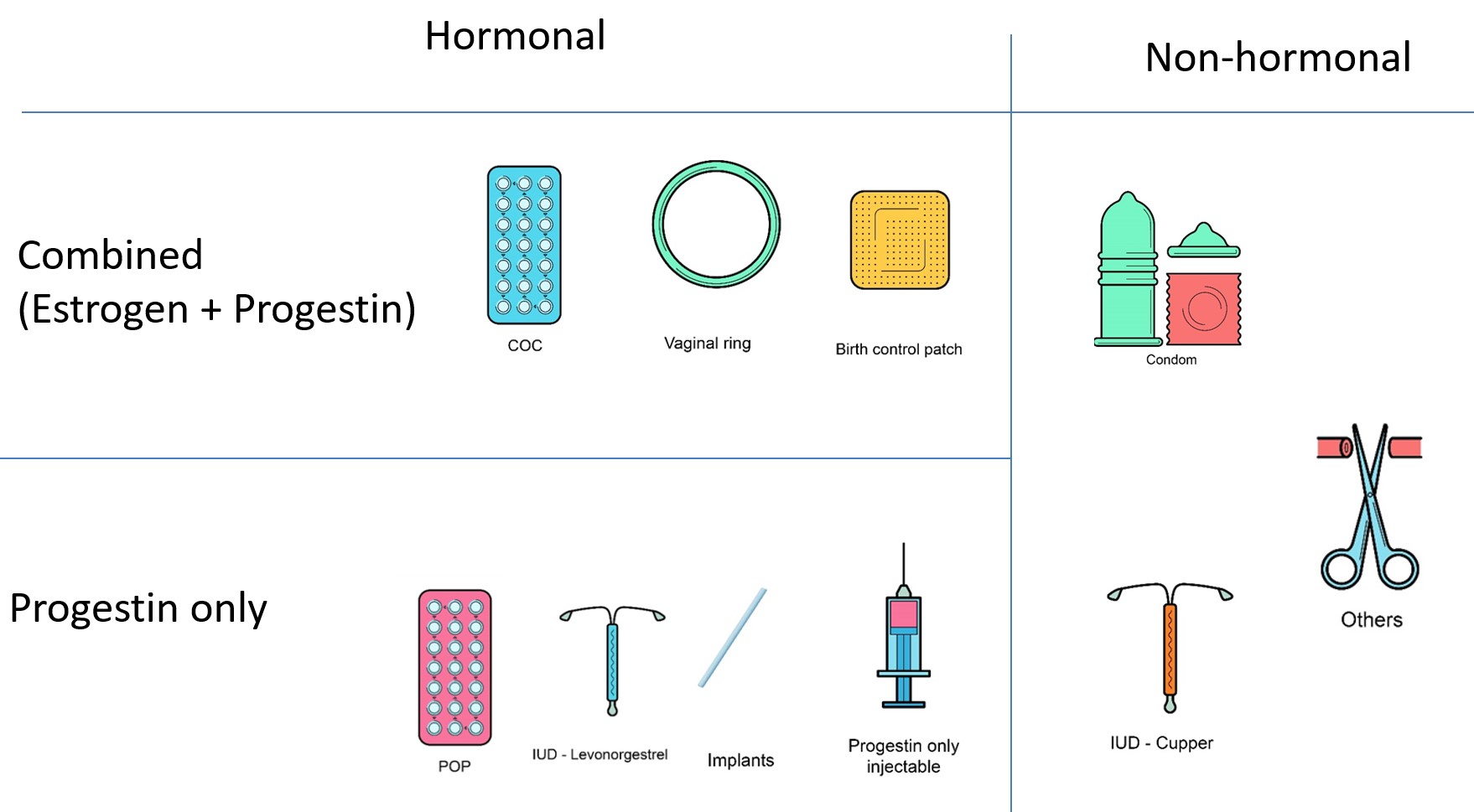
Click on a contraceptive to see information about it.
| Condom | |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 18% |
| Use | Forms a barrier to prevent sperm and egg from meeting/fertilizing |
| Side effects | Latex allergy (Latex free available) |
| Contraindications | None |
| Comments/benefits | Protects against STD´s, including HIV |
| IUD – Copper (5 years usually) | |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 0.8% |
| Use | Insert into the uterus
Copper component affects sperm motility and survival and prevents the sperm from fertilizing the egg |
| Side effects | Perforation of uterus/cervix: 1-2 in 1000 PID: less than 1%. Expulsion: 5% Irregular bleedings are common in the beginning 50 % chance of increased dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia |
| Contraindications | Known or suspected pregnancy PID Cancer in cervix or corpus uteri Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding |
| Comments/benefits | Normal menstrual cycle Can be used as emergency contraception (inserted within 7 days after unprotected intercourse) Before insertion: |
| OTHERS | |
|---|---|
| Sterilization permanent contraception |
Vasectomy (male) - Pearl index 0.15%
Tubal ligation/salpingectomy (female) |
| Lactational amenorrhea method (LAM) | Temporary contraception for new mothers; requires full breastfeeding day and night of an infant less than 6 months old - Pearl index 1-2% - prevents ovulation |
| Emergency contraception(ECP) within 5 days of unprotected sex; should be taken as early as possible |
ECP containing ullipristal acetate (Ellaone®)
ECP containing levonorgestrel (Postinor®, Norlevo ®)
COC (“Yuzpe method”) Copper bearing IUD (inserted within 7 days after unprotected intercourse) |
| Withdrawal (coitus interruptus) | Ejaculation outside the vagina, keeping the semen away from the partner´s external genitalia - Pearl index 22% |
| Standard Days Method (SDM) | Women track their fertile periods using cycle beads or other aids; avoiding unprotected sex during most fertile days - Pearl index 24% |
| Combined oral contraceptives (COC) = estrogen + progestin | Sold in Norway e.g.: Microgynon®, Loette®, Synfase®, Mercilon®, Zoely®, Qlaira®, Yasmin®, Yasminelle® |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 9% |
| Use | Must remember to take the pill every day Prevents the release of eggs from the ovaries |
| Side effects | Mild: Headache, nausea, mood changes/depression, spotting, bloating, breast tenderness, decreased sex drive Severe: Venous- or arterial thrombosis
|
| Contraindications | Previous venous- or arterial thrombosis Current breast cancer Migraine with aura Diabetes with nephron- or neuropathy Hypertension Liver cirrhosis Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) Reduced effect of COC if medication for epilepsy |
| Comments/benefits | Reduces menorrhagia and PMS (Premenstrual Syndrom) Reduces dysmenorrhea (treating endometriosis and adenomyosis) Reduces acne and hirsuitism if PCOS Decreased risk of endometrial, ovarian and colon cancer Long menstrual cycles is an option |
| Progestin-only pill (POP) | Sold in Norway e.g.: Cerazette®, Desogestrel® |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 9% |
| Use | Must remember to take the pill every day, POP is taken continuously without a break
Suppressing ovulation |
| Side effects | Mild: Bloating, nausea, breast tenderness, spotting, irregular bleedings, amenorrhoea, acne, mood changes/depression
Severe: none |
| Contraindications | Breast cancer |
| Comments/benefits | Can be used while breastfeeding Can reduce migraine Reduces dysmenorrhea Many women experience amenorrhea, others may have irregular bleeding. |
| Vaginal ring (COC vaginal insert) | Sold in Norway e.g.: Nuvaring® |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 9% |
| Use | The ring can stay in the vagina during intercourse Needs to be changed every 3 weeks
Prevents ovulation (release of eggs from the ovaries) |
| Side effects | Headache, nausea, mood changes, disturbances in menstrual bleeding patterns, pimples, decreased sex drive |
| Contraindications | Previous venous- or arterial thrombosis Current breast cancer Migraine with aura Diabetes with nephro- or neuropathy Hypertension Liver cirrhosis Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) |
| Comments/benefits | Often less side effect than COC Reduces dysmenorrhea Thrush or bacterial vaginosis can be harder to treat Long menstrual cycles is an option |
| IUD- Levonorgestrel | Sold in Norway e.g.: Mirena® (5 yrs), Levosert® (5 yrs), Kyleena® (5 yrs), Jaydess® (3 yrs) |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 0.2% |
| Use | Inserted into the uterus
Releases small amounts of Levonorgestrel each day |
| Side effects | Perforation: 1-2 in 1000 PID: less than 1%. Removal is not routinely required. Expulsion: 5% Irregular bleedings are common in the beginning Heavier bleedings for some users Differing progestin levels (high and low dosed) with differing risk of side effects (e.g. depending on gestagen doses) |
| Contraindications | Known or suspected pregnancy Known or suspected breast cancer PID Cancer in cervix or corpus uteri Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding Liver tumours, severe cirrhosis, or acute liver disease |
| Comments/benefits | Women who cannot use estrogen Changed bleeding pattern at 1 year of use: 50% amenorrhea 25% oligomenorrhea 11% spotting Mirena: Mirena and Levosert: Jaydess: Before insertion: |
| Birth control patch (COC patch) | Sold in Norway e.g.: Evra® |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 9% |
| Use | Important to replace the patch every week
Prevents ovulation (release of eggs from the ovaries) |
| Side effects | Breast tenderness, headache, nausea, mood changes, disturbances in bleeding patterns, pimples, decreased sex drive |
| Contraindications | Previous venous- or arterial thrombosis Current breast cancer Migraine with aura Diabetes with nephro- or neuropathy Hypertension Liver cirrhosis Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) |
| Comments/benefits | Reduces dysmenorrhea Long menstrual cycles is an option |
| Progestin-only injectable | Sold in Norway e.g.: Depo-Provera® |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 6% |
| Use | Injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously every third month
Suppressing ovulation |
| Side effects | Weight gain, irregular vaginal bleedings, osteoporosis, headache, acne, breast tenderness |
| Contraindications | Breast feeding (first 6 weeks) Ischemic heart disease or stroke Hypertension Multiple risk factors for fractures and osteoporosis Multiple risk factors for heart disease Severe celiac disease (osteoporosis) Diabetes with nephro- or neuropathy Breast cancer |
| Comments/benefits | Reduces menorrhagia Reduces dysmenorrhea (treating endometriosis) Many people lose their bleedings completely (50% after the first year) Delayed return to fertility |
| Implant (progestin- only), 3 years | Sold in Norway e.g.: Nexplanon® |
|---|---|
| Pearl index | 0.05% |
| Use | Placed under the skin of the upper arm
Primarily prevents ovulation |
| Side effects | Delayed fertility (about 1–4 months on average) after use Changed bleeding pattern: 1/3: regular bleedings 1/3: Irregular bleedings 1/3: no bleedings Method specific side effects: Nerve or vascular injury, deep insertion, non insertion |
| Contraindications | Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding Liver tumours, severe cirrhosis, or acute liver disease |
| Comments/benefits | Highest efficiency |
| Special care group | ||
|---|---|---|
| Postpartum & Breastfeeding |
Progestin-only pill (POP) and implant. After 6 weeks: Can also choose progestin injection After 6 months: Can also choose combined oral contraceptive (COC), patch and vaginal ring Directly postpartum IUD insertion (chosen in several low-income countries with poor access to postpartum health care) |
Estrogen may suppress lactation Estrogen increases risk for venous thrombosis |
| Postpartum & Not breastfeeding |
All progestin contraception After 6 weeks: COC, patch and vaginal ring |
Be aware of increased risk of venous thrombosis (especially the first 5-6 weeks postpartum) |
| Epilepsy (women who are on antiepileptic drugs) | IUD, progestin injection or implant |
Some antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) may make COC less effective Estrogen may make some AEDs less effective |
| After abortion |
Surgical: All contraception methods can be started the same day Medical: All methods | |
| Breast cancer | Non hormonal | Hormonal receptor- negative breast cancer & cancer- free after treatment: Can use any method (consult oncologist) |
| Diabetes mellitus (DM) |
All progestin methods (Progestins may effect insulin resistance, therefore cautious blood sugar control the first months of use with medroxyprogesteronacetat (Cerazette)) Non–vascular DM:
DM with vascular complication, DM for more than 20 years or DM with risk for arterial vascular disease: | Estrogen increases risk for thrombosis |
| Women with increased risk of venous or arterial thrombosis (Previous thrombosis, inherited disorder for thrombosis, hypertension, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, DM, BMI > 30) | All progestin | Estrogen increases risk for thrombosis |
| Dysmenorrhea Endometrioses (and adenomyosis) |
IUD – Mirena Progestin injection POP Progestin implant COC - recommend that the pill is taken daily continuously for effect on pain (achieve amenorrhea) | Achieve amenorrhea |
| Menorrhagia |
IUD- Mirena, Levosert COC | |
| Migraine |
All progestins. The POP/COC may reduce migraine- related attacks Migraine with aura: Migraine with no aura and < 35 yrs: | Estrogen is associated with a very small increased risk of ischemic stroke |
| How does it work? | Extended regimen or continuous cycle COC reduces or eliminates the withdrawal bleeding that would occur every 28 days. It works by reducing the frequency of the pill- free or placebo days. It is an effective and safe option. |
| Patient groups | For women who suffer from hormone withdrawal symptoms and cyclical symptoms (e.g. headache, mood changes, dysmenorrhoea, heavy menstrual bleeding) For women who want to reduce the interference of scheduled bleeding with daily activities, such as sexual activity, exercise, sports and work. |
| Efficacy | The contraceptive efficacy of extended regimen COC is comparable to that of conventional 28-day (i.e., 21/7) regimens. |
| POP Cerazette® | Should be taken within 12 hours if forgotten (within 36 hours after the last pill) |
| POP Conludag® mini pill | Should be taken within 3 hours if forgotten (within 25 hours after the last pill) |
| COC | Should be taken within 24 hours if forgotten (within 48 hours after the last pill) |
| Emergency contraception (ECP) |
Within 5 days of unprotected sex; should be taken as early as possible ECP containing ullipristal acetate (Ellaone®)
ECP containing levonorgestrel (Postinor®, Norlevo ®)
COC (“Yuzpe method”)
Copper bearing IUD
|