Venous Thromboembolism (VT)
Incidence and prognosis
Pregnancy is a state of hypercoagulability due to an increase in procoagulant and a decrease in anticoagulant and fibrinolytic activity. This hypercoagulation prevents large bleeding postpartum when placenta detaches from the uterine wall. 1 / 1000 pregnant women will experience Venous Thromboembolism (VT) either as Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) or as Pulmonary Embolism (PE). Pregnancy increases the risk of VT 10-fold. If diagnosed and treated, the prognosis is good for both mother and child and future pregnancies.
If undiagnosed and untreated, it is one of the leading causes of maternal death.
The highest absolute risk of pregnancy-associated venous thrombosis is the first 6 weeks postpartum, but the thrombosis can occur already in the first trimester. The figure below shows the distribution of VTs throughout pregnancy and postpartum in a Norwegian population 1993-2003.
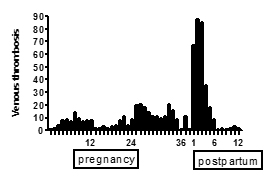
Jacobsen AF, Skjeldestad FE, Sandset PM. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:233.
Republished with permission from Elsevier.
Clinical Signs and Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VT).
The two most common presentations are Pulmonary Embolism (PE) and Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
A pregnant woman with an acute episode of severe shortness of breath (dyspnea) combined with tachycardia should be suspected of having a pulmonary embolism. Appropriate diagnostics should be performed.
- If symptoms of a DVT: start with an ultrasound/ Doppler of the lower extremities. This diagnostics is preferred due to lack of radiation. If a DVT is diagnosed, there is no need to confirm with pulmonary CT scan. If ultrasound/Doppler is negative and your suspicion of PE is strong, you will continue with an examination of the lungs:
- Pulmonary CTPA scan or a perfusion scintigraphy.
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
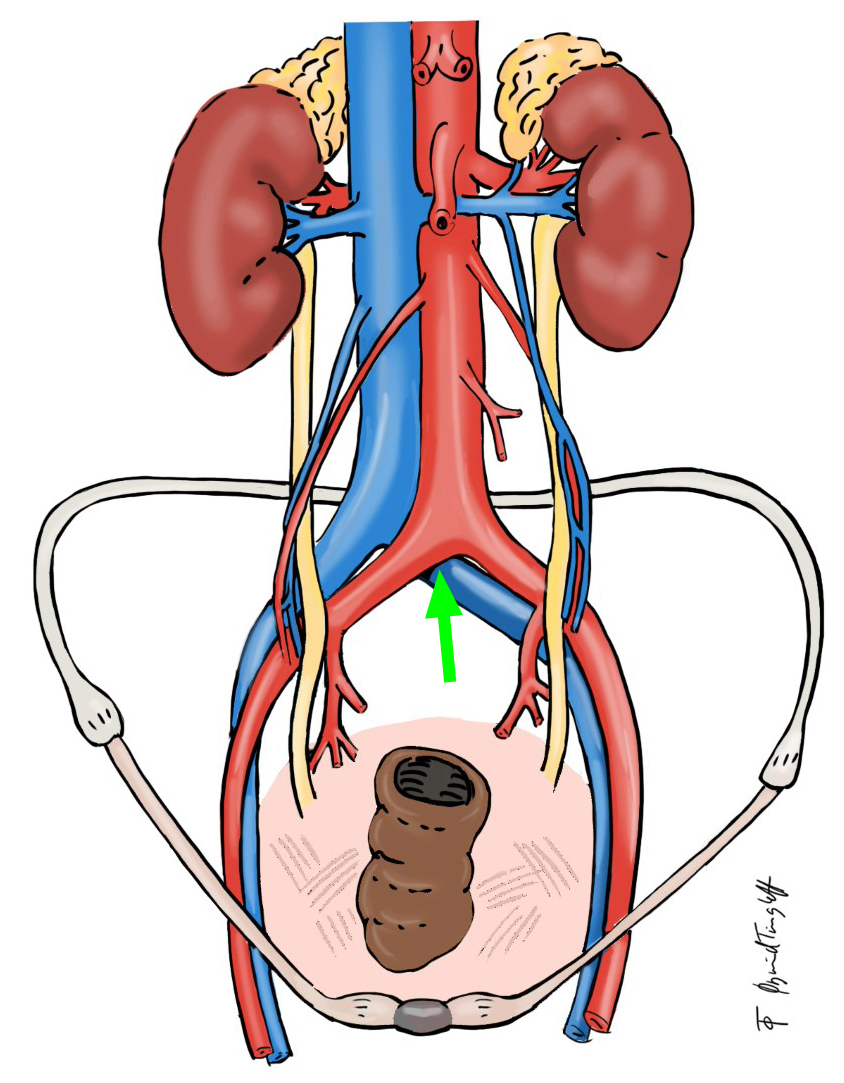
Pregnancy associated deep venous thrombosis are left-sided in 80-90%. The right iliac artery crosses the left iliac vein and causes compression of this vein (see figure below). Furthermore venous stasis is increased by compression from the gravid uterus.
75 % of the DVTs will be proximal (above the knee). Most DVTs will be located in the left inguinal area (see figure below) and present with vague and atypical thrombotic clinical signs, like low left-sided abdominal or groin pain. It might also present with low back pain and after some days there will be swelling of the thigh. Sometimes, women with DVT will also have symptoms in the leg.
Diagnose DVT with ultrasound/Doppler.
Summary of Clinical signs and Diagnosis
| Clinical signs | Diagnosis |
|---|
| Pulmonary Embolism (PE) | Dyspnea, tachycardia, pain, tachypnea, hemoptysis | Ultrasound/Doppler of lower extremities. (If negative ultrasound/Doppler: CT pulmonary scan or Perfusion Scintigraphy) |
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
80-90% left sided and proximal | One-sided low abdominal pain, groin pain and/or swelling of the lower extremity (mainly thigh) | Ultrasound /Doppler (MRI might be used if challenging imaging) |
Treatment of PE and DVT
- Low molecular weight heparin (LMVH) injection subcutaneously (sc) daily the whole pregnancy and 6-12 weeks postpartum
- LMVH does not pass the placenta and does not affect the baby
- LMVH can be used during breast feeding
- Stop treatment in labour, vaginal delivery is recommended
- Next pregnancy: Prophylactic anticoagulation ( LMVH inj sc) from 1. trimester throughout pregnancy and 6 weeks postpartum
Risk factors for PE and DVT
- Previous venous thrombosis
- Family history of venous thrombosis (first degree relative with VT <50 years old)
- Thrombophilia s (factor V Leiden, Prothrombin mutation, Prot S, Prot C or Antithrombin deficiencyor antiphospholipid antibodies)
- Clinical risk factors : immobilization, ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome (OHSS) , obesity, infection, hemorrhage, blood transfusion, surgery, varicose veins
What to tell a patient with risk for pregnancy DVT?
Would you be able to answer all the questions this patient asks in this movie?
Take home message
- Pregnancy is a hypercoagulable state
- DVT symptoms in pregnancy are often low left-sided abdominal pain or groin pain
- Acute dyspnea in pregnancy is pulmonary embolism until other diagnosis is confirmed
- VTE is one of the leading causes of maternal deaths


